Read in this article:
- What is air humidity and what does it depend on?
- Humidity standards
- How to determine air humidity?
- Why is low humidity dangerous?
- How to maintain normal humidity?
- Low air humidity and health
Indoor air humidity is an important component of the microclimate, which affects not only a person’s comfort, but also his health. A long stay in a room with high or low humidity can cause poor health and even some diseases. That is why it is necessary to know how to determine this indicator and, if necessary, change the amount of moisture contained in the air.
What is air humidity and what does it depend on?
The air we breathe always contains a certain amount of moisture in the form of water vapor. If the humidity level reaches 100%, the air can no longer hold as much water. Then it settles on surfaces in the form of condensation or it starts to rain. Accordingly, a humidity of 50% means that the surrounding air contains exactly the same percentage of the maximum amount of moisture that it can hold.
Humidity directly depends on temperature: the hotter the air, the lower it is. There are other factors that influence this indicator:
- Ventilation – forced supply systems facilitate the flow of air into the room, which causes the relative humidity in it to decrease;
- Weather outside - in the cold winter months the air is drier, on rainy days the humidity is higher (air from the street gets indoors in any case);
- Heating – radiators and heaters simultaneously increase the air temperature and activate natural ventilation, which contributes to low humidity;
- Air conditioners - the use of such devices, even in cooling mode, dries the air, since it collects moisture in condensation and removes it through drainage pipes;
- Plastic windows and insulated walls impair ventilation, so humidity increases.
The level of humidity is affected by where you live - near bodies of water the indicator is higher. Living conditions also play a role. For example, if a large amount of laundry is often dried in an apartment after washing, this will contribute to an increase in humidity. The same goes for cooking without a hood. True, in these cases the indicator does not increase too noticeably and for a short time.
Oxygen starvation
Have you noticed that at some moments we feel sleepy or just tired, even though we haven’t done any physical work? The fact is that when the ambient air humidity is low, our blood absorbs oxygen more slowly . As a result, our body suffers from oxygen starvation and performance decreases.
At the same time, if you start humidifying the air, at least using improvised methods, fatigue will go away as if by hand..
Humidity standards
The optimal humidity level is considered to be 45-60%. But this is an average and may vary depending on certain conditions. For example, in the cold season the norm is 30-45%, and in the warm season – 30-60%.
Normal air humidity is determined separately for each room:
- In the dining room, kitchen or bathroom, a humidity of 40-60% is allowed, since such rooms have sources of moisture that are often used;
- In the children's room it is recommended to maintain the indicator within 45-55%;
- For the bedroom, the optimal humidity is 40-50%;
- In a library, it is not advisable to allow humidity to rise above 40%, as this may adversely affect books.
In general, it is generally accepted that 30% or less is low air humidity, and above 65% is high. Both options are harmful to the body.
What needs to be done to make the air in the apartment optimal.
The temperature of the room has a great influence on the feeling of humidity. The warmer the air, the more water it absorbs. When calculating relative humidity, do not forget that in the presence of high temperatures, the volumes of liquids in these quantities of air will become smaller. Knowing this allows you to maintain normal humidity levels by ventilating the room in winter. In this way you can achieve optimal parameters.
Absorbs moisture:
- heating elements;
- soft toys, furniture, rugs, carpets;
- air conditioners.
Sources of moisture:
- aquariums;
- house plants;
- wet tissues;
- water boiling when cooking food;
- leaking and faulty plumbing.
How to determine air humidity?
So, to create an optimal microclimate in terms of humidity, you need to solve two issues: determine the current indicator and take measures that will allow you to regulate it. The easiest way to measure is with a hygrometer. There are different types of such devices, the most convenient for domestic use is electronic. The display shows humidity indicators, and in many models also temperatures.
But not everyone has a hygrometer at home, so the question may well arise of how to determine the air humidity in a room without instruments. There are several ways to do this:
- Using a glass of water, place the container in the refrigerator and wait until the temperature of the liquid reaches +5°C. Then you need to place the glass in the room and watch for condensation. If water droplets form on the walls within 10-15 minutes, then the air is dry. If it takes longer, the humidity is normal or high. It is worth considering that this is a very approximate result;
- Using a thermometer, you need to measure the temperature in the room and write down the reading. Then wrap the device head with a moistened cloth or cotton wool and see what the temperature will be after 10 minutes. The second indicator should be subtracted from the first indicator and the result assessed using the Assmann table;
- The most exotic way is with the help of a fir cone that recently fell from a tree, but did not have time to dry out. The cone must be placed at a considerable distance from radiators and air conditioners, and then observed. If the scales are pressed towards the middle, the humidity is excessive; if they protrude, the humidity is insufficient.
Drying house plants indicate low humidity in the apartment. But none of the listed methods guarantees an accurate result. It is best to use a hygrometer.
Why is air humidification necessary?
People, materials and products require their own specific air humidity. If the relative humidity is too low, water from the surface layers will move into the air. As a result, people will have dry lips and skin, less resistance to various viruses, wood will dry out and crack, paper will become deformed. This list is quite long. It is important that users understand the effect that insufficient air humidification can have in a particular situation. Because often they don't realize it!
Relative humidity (RH%) is not usually measured. It is not related to specific problems experienced by the user. Letting the client know how much he will gain through proper air humidification is the first step for us in the communication process.
The second step is to show the client that since the humidification system provides important practical results, it is not worth buying the cheapest system. The customer should get a fair return on their money: low power consumption, reliability and high efficiency. Most inexpensive household systems are physically unable to cope with the task due to low performance, several times less than the calculated values.
The third step is to inform the client about the possible health risks that a poorly designed system poses (fungus, legionella and other microorganisms). Rotary mechanisms and ultrasonic systems that promote the rapid growth of microorganisms pose a serious risk to human health. This is the third argument why the buyer should pay attention to safe systems.
Why is low humidity dangerous?
A person consists of an average of 60% water, so low humidity is very dangerous for the body. Excessive dry air causes many negative phenomena:
- Irritation of the mucous membranes of the throat and nasal cavity - dry surfaces crack, opening access to harmful microorganisms;
- Static electricity is generated in the room, causing dust particles to rise into the air. This provokes the spread of bacteria, dust mites, allergic manifestations;
- Nails and hair dry out, the skin loses elasticity, premature wrinkles, dermatitis, peeling, and microcracks appear;
- Dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyes results in unpleasant itching;
- The blood gradually thickens, its movement slows down, and the person begins to feel weak. At the same time, the load on the heart increases noticeably;
- The viscosity of fluids in the body increases, for example, gastric and intestinal juices, which causes disruptions in the digestive system;
- Constantly inhaling dry air through the nose leads to pain and bleeding.
Low humidity is especially dangerous for children, because they have more sensitive skin and respiratory systems than adults. In rooms with dry air, a child may develop a cough; his body becomes more susceptible to virus damage due to decreased immunity and dry mucous membranes.
Recommendations!
The human body can adapt to any temperature regime, but why should it “hurt” it? To prevent us from feeling thirsty, we need to drink at least 2-2.5 liters of water a day, eat liquid meals, moisturize the body in a timely manner, take baths, contrast showers, and make special masks for the skin of the body and hair.
If there is sufficient humidity in the room, then you and your family will be able to more easily endure seasonal colds, cough less and not be influenced by allergic pollen pathogens.
Take care of your home and love it! Happiness and prosperity to you!
How to maintain normal humidity?
If the humidity level in the room is too low, the best solution is to use a special device - a humidifier. There are several types of such devices:
- Traditional - a special reservoir is filled with water, which then goes to the filter or cartridge. The fan drives air through them and returns it to the room cleaned and humidified;
- Steam - the water is heated, the air is saturated with moisture due to hot steam;
- Ultrasonic - the hearth is fed onto a plate that vibrates under the influence of ultrasound. The dispenser sprays water in the form of microscopic particles that are held by air molecules.
Humidifiers have many useful additional functions: they automatically turn off, can work as fragrances, purify the air using filters, and switch to quiet night mode. But their main advantage is the ability to quickly increase air humidity to a normal level and maintain it for a long time.
Information for the public
The influence of air humidity on human health
Weather and climate conditions intensively influence people’s well-being and can improve or worsen our health.
An important parameter from this point of view is air humidity. Air humidity is determined by the amount of water vapor contained in it. To indicate the level of air humidity, there are such concepts as: - absolute humidity, measured in g/m3 (shows how many grams of water one cubic meter of air contains) and the more familiar and easier to understand - relative humidity, measured in % (shows the degree of saturation air with water vapor). The ability of air to hold water vapor in one quantity or another determines our concepts of “dry” and “wet” air. “Dry” air is considered to be one that is capable of absorbing a fairly significant amount of water vapor in order to reach a state of saturation, and “wet” air is one that, with a slight increase in water vapor, is saturated with this vapor. Air with a relative humidity of less than 55% is considered dry, from 56% to 70% moderately dry, from 71% to 85% moderately humid, and above 85% very humid. Acceptable values of relative air humidity range from 30 to 70%. The optimal values of relative air humidity in average climatic conditions, which have a beneficial effect on our health, lie in the range from 40 to 60% at a temperature of 18-24°C. Of course, the level of humidity depends on factors such as the time of year (in the warm season, humidity levels are higher than in the cold), geographic location, and the presence of large bodies of water. The hygienic value of air humidity is associated with its influence on the heat exchange between a person and the environment. The process of heat transfer by the human body through sweating directly depends on the degree of saturation of the air with water vapor.
High humidity (more than 85%) complicates heat exchange between the human body and the external environment due to reduced evaporation of sweat from the surface of the skin. The higher the humidity, the less sweat evaporates per unit time and the faster the body overheats, which at a minimum entails lethargy and nausea, and at a maximum, loss of consciousness, heart attacks, and oxygen starvation of the brain. High humidity at ambient temperatures above 30°C has a particularly unfavorable effect on a person’s thermal well-being, since almost all of the heat released is released into the environment through the evaporation of sweat. When humidity increases, sweat does not evaporate, but flows down in drops from the surface of the skin; a so-called “heavy” flow of sweat occurs, exhausting the body and not providing the necessary heat transfer. High humidity is also dangerous in combination with low temperature, as there is a risk of severe hypothermia. At the same time, moderately humid air can be very beneficial for health; it has a beneficial effect on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, helps clear mucus, and protects against pathogenic bacteria.
Insufficient air humidity (less than 20%) also has a negative impact on human health due to intense evaporation of moisture from the surface of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, which can lead to their drying out and cracking, and then contamination by pathogenic microorganisms. At this level of humidity, even healthy people experience a feeling of dryness in the nasopharynx, “stinging” in the eyes, and nosebleeds may begin. Too dry air is especially dangerous for patients with bronchial asthma; they experience a general deterioration in their health, and attacks are possible. On the other hand, moderately dry air makes it easier to tolerate low and high temperatures. For example, with low relative humidity, summer heat is more easily tolerated than the same temperature in areas with high humidity. It's the same with negative temperatures. Severe frosts with low humidity bring much less discomfort than a slight “minus” in humid air conditions.
We spend most of our lives in various rooms, and our well-being and performance depend on how comfortable the microclimate is in our apartment, office, classroom. In the Russian Federation, the basic hygienic requirements for microclimate parameters in residential and public premises are established in the following documents:
- SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises”;
- GOST 30494-2011 “Interstate standard. Residential and public buildings. Indoor microclimate parameters."
According to the requirements of these documents, in living rooms (including dormitories), premises of public and administrative buildings, the optimal relative air humidity should be in the range of 45-30% in the cold season and in the range of 60-30% in the warm season. Such humidity levels ensure the normal functioning of the body, promote hydration of the skin and mucous membranes, and to some extent maintain the constant humidity of the internal environment of the body. Permissible relative humidity is 60% in the cold season and 65% in the warm season. It should be noted that such humidity levels are favorable not only for humans, but also for finishing materials, furniture, textile (carpets, curtains, etc.), paper (books, etc.) products, household appliances and other interior items, including and antique. For pets and most indoor plants, these humidity values are also suitable, but if your “green friend” is, for example, a representative of tropical vegetation and requires high air humidity (75-95%), then you need to “house” it in a specially equipped room ( greenhouse, winter garden).
For specialized premises (health care facilities, gyms, swimming pools, etc.), optimal and permissible standards for relative air humidity are established in separate regulatory documents.
Nowadays, manufacturers offer a fairly wide range of all kinds of instruments for measuring humidity in rooms (hygrometers, thermohygrometers, psychrometers, gyrostats, etc.), very different in price, design features and design, so it’s not at all difficult to control the humidity levels in your homes and offices, it’s more difficult maintain optimal humidity values.
What to do if the indoor air is too dry? Dry indoor air is a common problem, especially in multi-unit residential buildings. It may be due to the specifics of the building materials used in the construction of the building; malfunction of ventilation systems; in the cold season - by the operation of heating systems (a kind of “payment” for heat); excessive “sealing” of the premises due to the installation of double-glazed windows, and other reasons. There are many ways to humidify the air. The simplest and most accessible of them are:
- lowering the temperature in the heating system, if possible;
- frequent wet cleaning of premises;
- installation of containers filled with water near heating devices;
- regular spraying of the room (air and curtains) using a spray bottle;
- hanging wet towels or sheets on heating appliances;
- regular ventilation;
- growing some types of indoor plants (chlorphytum, aloe, ficus) which will not only help to humidify the air, but also cleanse it of harmful bacteria;
- installation of a large aquarium;
- For more “advanced” users, there is a huge variety of special devices - air humidifiers.
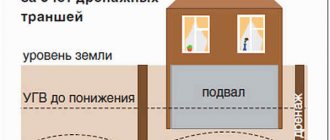
What to do if the indoor air is too humid? Excessive air humidity may be caused by defects in the roof or walls of the building; violations of isolation from groundwater; problems with water supply pipes; poor ventilation, especially in kitchens and bathrooms; violation of established hygienic standards for the volume of air per person, i.e., simply put, overcrowding. The problem of high indoor air humidity is less common, but has more serious consequences, both for the health of the occupants of the room and for the room itself, due to the risk of the formation and proliferation of mold, putrefactive bacteria and other microorganisms, which is also detrimental to health. If it is not possible to quickly solve the problem radically by eliminating its source, then special devices - air dehumidifiers - can come to the rescue.
Comfort and warmth to your home! Be healthy!
Signs of an incorrect microclimate
If you are observant, you can determine by eye what kind of microclimate reigns in the room. Excessively dry air is characterized by the following symptoms :
- flower pots
- objects in the room are electrified ;
- washed laundry dries in the house in 1-2 hours , and after that it has to be ironed with steam;
- Even after wet cleaning, the presence of the smell of dust in the room can be felt .
Indoor flowers with insufficient moisture quickly fade, and the foliage turns yellow at the edges. They grow poorly and often get sick, despite proper care.
If the proportion of water vapor in the air space is very high , the room becomes damp and musty .
- Clothes and items become damp and may smell musty .
- Washed laundry does not dry for a long time , acquiring a disgusting smell.
- The soil in flower pots after watering .
- In the kitchen salt left in an open salt shaker becomes damp and heavy .
- Doors swell and do not close tightly.
table 2
| OPTIMAL PARAMETERS | ACCEPTABLE PARAMETERS | ||
| Temperature deg. WITH. | Relative Humidity % | Temperature deg. WITH. | Relative Humidity % |
| 19 | 62 | 18 | 39 |
| 20 | 58 | 22 | 31 |
| 21 | 55 | ||
Note : air speed – no more than 0.1 m/s.
Knowledge of humidity in meteorology is of great importance for weather prediction.
Go to section: 2.2 Methodology and role of the experiment
Humidifiers for home use
When the problem of dry air in a home is acute, for example, someone has a tendency to allergies, then you need to buy a special device - a humidifier. There are 3 main types - steam, traditional and ultrasonic. Each type has advantages and disadvantages that should be fully considered before purchasing. The table contains comparative characteristics of common humidifiers.
| View | Structure | Advantages | Flaws |
| Traditional | Water container, filter and fan | Low electricity consumption, evaporation completes when optimal humidity is reached, does not break down when water is completely consumed | High frequency of replacement of filter components, it is necessary to use exclusively distilled or purified water, humidity cannot be adjusted (when the mark reaches 60%, the humidifier turns off automatically) |
| Steam | Water tank, fan, heating element, steam chamber, steam sprayer | Rapid increase in humidity levels, the ability to use tap water, no need to change filters, when the liquid boils away the device automatically turns off | Possibility of accidental burn due to carelessness, high energy consumption |
| Ultrasonic | Sprayer, vaporization chamber, ultrasonic membrane, fan, water tank and liquid softening chamber | Compact, economical, safe, ability to adjust humidity levels, rapid increase in performance, low price | Marks appear on the surface when pouring tap water |
All types of humidifiers are quite compact, but there are also built-in systems that are made of several devices that purify and humidify the air to a level specified by the owner. Some air conditioners also come with humidifiers. But, it is necessary to observe the measure and not increase the humidity in the living room above 70%. This indicator can also lead to diseases due to the creation of a favorable environment for pathological microflora.
Humidity affects sweating
unsplash.com
On particularly hot days, our body's ability to heal itself is greatly impaired. “You start to feel uncomfortable because the moisture in the air makes it harder for your body to produce sweat,” explains Christina L. Belicki, a certified nursing assistant at Northwell Health. “The evaporation of sweat on our skin is the body’s way of naturally cooling itself at high temperatures.”
In hot and humid weather, our sweat hardly dries, causing our body temperature to rise. This is why the air in a humid climate can feel very hot, but the same temperature in a dry climate is much better tolerated.
Perhaps this is why hot and humid weather also affects a person's mental health. An Australian study published in the international scientific journal PLoS One in 2016 found that the hotter and more humid the air, the more likely people are to experience mental health problems.
May lead to dehydration
Nickelodeon
Constant sweating in hot weather can be very uncomfortable: think about your feet sticking to leather seats.
But at the same time, this can lead to more negative consequences - dehydration. “When you sweat, you lose important electrolytes for the body, such as sodium and chloride,” explains Dr. Nesheiwat. “Therefore, it is very important to maintain fluid balance in the body to avoid fainting, muscle cramps and overheating, especially in the summer.”
So don't forget to drink as much water as possible when the thermometer goes off scale and the air humidity rises.