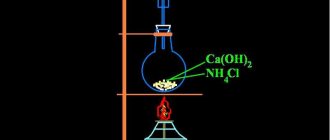
What is phosphoric acid
At room temperature these are hygroscopic, colorless, diamond-shaped crystals that are highly soluble in water. An orthophosphoric compound is considered an inorganic acid of medium strength. One of its forms is a yellowish or colorless syrupy liquid, odorless, an aqueous solution with a concentration of 85%. Its other name is white phosphoric acid.
The chemical orthophosphorus compound has the following properties:
- soluble in ethanol, water, solvents;
- forms 3 rows of salts - phosphates;
- causes burns upon contact with skin;
- when interacting with metals, it forms flammable, explosive hydrogen;
- the boiling point depends on the concentration - from 103 to 380 degrees;
- the liquid form is prone to hypothermia;
- incompatible with flammable materials, pure metals, quicklime, alcohol, calcium carbide, chlorates;
- at a temperature of 42.35 degrees it melts, but does not decompose.
Harm to the body
Officially, phosphoric acid is recognized as completely safe for human health and is approved for use in different countries around the world, but scientific practical data indicate the presence of harmful consequences for the body of living beings. The product is non-toxic and does not lead to negative consequences when consumed in small quantities. It can cause the development of caries, which arises from a violation of the integrity of the top layer of enamel when it comes into contact with sugar crystals. The resulting environment is favorable for the life of bacteria in the oral cavity. Phosphoric acid is in demand in the production of carbonated drinks, baked goods, sausages and processed cheeses, the use of which leads to a violation of the acidity level. The body's protective functions begin to restore the alkaline balance using calcium taken from bones and teeth. A lack of calcium compounds leads to pain in the joints and destruction of the integrity of the teeth. A solution of orthophosphoric acid with a concentration of more than 50%, if the technology and process control are not followed, causes:
- burns of mucous membranes and skin;
- the occurrence of bloody discharge from the nose;
- dental problems;
- abnormalities in the blood count;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea caused by a malfunction of the digestive tract.
With prolonged action of a food additive on the body, a person loses the sense of appetite, which leads to sudden weight loss and health problems. If you have diseases of the intestinal tract, the use of products with the food additive E338 should be completely excluded from the diet.
Formula
Phosphoric acid is an inorganic compound that is described by the formula H3PO4. Its molar mass is 98 g/mol. A microparticle of a substance is built in space in such a way that it connects hydrogen and oxygen atoms with each other. The formula shows that the chemical substance has the following composition:
| Number of atoms | Mass percentage | |
| Hydrogen | 3 | 3,1 |
| Phosphorus | 1 | 65,3 |
| Oxygen | 4 | 31,6 |
Areas of use
Phosphoric acid and its derivatives have found wide application in a wide variety of areas of human life. Among the main directions are:
Production of simple phosphorus (superphosphate and phosphate rock), complex and complex mixed fertilizers.- The use of feed phosphates as one of the important additives in agriculture makes it possible to increase the average daily weight gain in pigs and bulls, and increase milk productivity and egg production.
- Esters and salts are widely used in the manufacture of additives for water softening and synthetic detergents, and are part of surfactants in the manufacture of cement. They bind calcium and magnesium ions, which are responsible for hardness and worsen the quality of washing.
- In foundry production and metalworking, orthophosphoric acid has been used for rust - for phosphating, as a flux for soldering on stainless steel, ferrous metals and oxidized copper, for polishing and cleaning surfaces.
- In the textile industry - for fire-retardant impregnation and dyeing of wool and leather, natural and synthetic fibers.
- In chemical production, it serves as a catalyst for organic synthesis and raw material for reagents.
- In the aerospace field, its esters are components of the hydraulic fluid of aircraft engines and rocket fuel deicers.
- In the mining and oil industries, sodium phosphates are used to enrich ores and prepare drilling slurries.
- In freezing units it is part of freon. It is also used for the manufacture of various brands of special glasses, including optical glasses, ceramics and porcelain, photosensitive emulsions for photographic paper and film.
- In the production of refractories, phosphates serve as fillers for refractory concrete, raw materials for phosphorus wood boards and non-combustible foam, fire-resistant paints and materials (varnishes, paints, enamels, primers and impregnations).
- In medicine, its solutions are used to prevent urolithiasis and stomach problems. In dentistry, it is used for the manufacture of cements, compositions for etching tooth enamel and treating the internal surfaces of crowns.
- The woodworking industry has found application in the fact that impregnation with phosphoric acid makes the material non-flammable - it imparts fire resistance. For example, when making matches, aspen sticks are impregnated with a 1.5% solution to prevent smoldering.
- In the food industry, the E338 additive regulates acidity, increases shelf life, preserves flavor characteristics and enhances the effect of antioxidants. It is widely used in baking powders, processed cheeses, carbonated drinks, baby formula, marmalade and cakes, sausage production and sugar production.
Preparation of phosphoric acid
A chemical compound has several production methods. The well-known industrial method for producing phosphoric acid is thermal, which produces a pure, high-quality product. The following process occurs:
- oxidation during combustion with excess air of phosphorus to phosphorus anhydride having the formula P4O10;
- hydration, absorption of the resulting substance;
- condensation of phosphoric acid;
- capturing mist from the gas fraction.
There are two more methods for producing orthophosphorus compounds:
- An economical extraction method. Its basis is the decomposition of natural phosphate minerals with hydrochloric acid.
- Under laboratory conditions, the substance is obtained by reacting white phosphorus, which is toxic, with dilute nitric acid. The process requires strict adherence to safety precautions.
Mineral fertilizers based on orthophosphoric acid
The use and consumption of mineral and phosphate fertilizers is growing steadily throughout the world. One of the most popular are fertilizers based on phosphoric acid.
According to the International Fertilizer Association (IFA), consumption of phosphate-containing fertilizers reached 40 million tons per year in 2010. And it continues to grow by several million every year.
The International Fertilizer Association (IFA) is a non-profit association dedicated to the study and use of fertilizers in industry, the promotion of plant nutrients to markets around the world, and improving the environmental situation in countries where the use of pesticides is at a very high level. The company was founded in 1927, its headquarters are located in Paris, but its employees are in the most direct conditions of working with fertilizers - fields and factories. The company has about 600 members from 85 countries.
The basis for mineral and phosphate-containing fertilizers, of course, is phosphoric acid. 90% of all phosphorus-containing ore goes to this area. Among the world's manufacturers: China, USA, Morocco, Russian Federation
Phosphorus fertilizers are mineral fertilizers containing calcium salts, superphosphate, ammophosphate, orthophosphate, metaphosphate, phosphate rock and other derivatives of ammonium phosphoric acid.
The popularity of phosphorus-containing fertilizers is associated with their relative safety. Phosphorus is found naturally in plant growth and is responsible for important functions of growth and maturation. It is phosphorus in plants that is responsible for the plant’s resistance to difficult conditions, increasing frost resistance, accumulation of sugar, fat, and starch. Phosphorus fertilizers are the only source of phosphorus in the soil, responsible for all these functions.
The largest exporters of phosphate-containing fertilizers are the following countries (according to 2010 data):
- USA (volume 3,942,216 tons in terms of phosphate P2O5).
- Russian Federation (volume 1,566,495 tons in terms of phosphate P2O5).
- China (volume 1,560,720 tons in terms of phosphate P2O5).
- Tunisia (volume 803,351 tons in terms of phosphate P2O5).
- Morocco (volume 708,101 tons in terms of phosphate P2O5).
While the list of the main suppliers of phosphoric acid to the world market is as follows:
- Morocco – 6 million tons.
- South America – 1.1 million tons.
- USA – 0.8 million tons.
- China – 0.5 million tons.
More information about production and sales markets can be found in the article: “Production and sale of orthophosphoric acid”
Chemical properties
The inorganic compound is considered tribasic and of medium strength. The following chemical properties of orthophosphoric acid are characteristic:
- reacts to indicators by changing color to red;
- when heated, it is converted to pyrophosphoric acid;
- in aqueous solutions undergoes three-stage dissociation;
- when reacting with strong acids, it forms phosphoryls - complex salts;
- forms a yellow precipitate when interacting with silver nitrate;
- thermally decomposes to diphosphoric acid;
- upon contact with bases, amorphous hydroxides, it forms water and salt.
Production process
In laboratory conditions it is obtained:
- Dissolving phosphorus (V) oxide in water when heated.
- Hydrolysis of phosphorus pentachloride in hot water.
- When concentrated nitric acid reacts with white phosphorus.
The industry uses thermal and extraction (sulfuric acid) methods. The thermal method, which allows to achieve the greatest purity of the product, includes the following stages:
- Oxidation of elemental phosphorus by combustion in excess air to produce tetraphosphorus decaoxide (phosphoric anhydride).
- Hydration and absorption of its vapors in special towers.
- Condensation of the resulting acid with the capture of mist from the gas phase.
The extraction method uses the reaction of sulfuric acid decomposition of natural salts with a yield of up to 95%. Process stages:
- A mixture of sulfuric acid and natural phosphate, the so-called. The pulp is fed from the hopper into the extractor - a steel lined vat with a stirrer.
- In 4 hours, the pulp heated to 90 °C successively passes through several such reactors. As a result, phosphoric acid is formed and calcium sulfate crystallizes.
- To separate, the pulp enters a perforated belt with a filter cloth, and through its holes the finished product is collected into a vacuum chamber.
Application
Phosphoric acid is used in many areas, from industry to dental treatment. The product is used by craftsmen as a flux when soldering, to clean the metal surface from rust. Liquid is used:
- for scientific research in molecular biology;
- as a catalyst for organic synthesis processes;
- for creating anti-corrosion coatings on metals;
- in the production of fire-resistant impregnations for wood.
The substance is used:
- in the oil industry;
- in the manufacture of matches;
- for film production;
- for the purpose of protection against corrosion;
- to clarify sucrose;
- in the manufacture of medicines;
- in refrigeration units as a binder in freon;
- during mechanical processing for polishing and cleaning metals;
- in the textile industry in the production of fabrics with fire retardant impregnation;
- as a component in the production of chemical reagents;
- in veterinary medicine for the treatment of urolithiasis in minks;
- as a component for metal primer.
In the food industry
The use of phosphoric acid in food production has become widespread. It is registered in the register of food additives under code E338. When consumed in acceptable quantities, the substance is considered safe. The following properties of the drug are useful:
- preventing rancidity;
- acidity regulation;
- shelf life extension;
- preservation of taste characteristics;
- enhancing the effect of antioxidants.
Phosphoric acid as an acidifier, leavening agent, and antioxidant is used in the bakery, meat, and dairy industries. Used in the production of confectionery and sugar. The substance gives products a sour, bitter taste. Additive E338 is included in:
- processed cheeses;
- muffins;
- carbonated drinks - Pepsi-Cola, Sprite;
- sausages;
- buns;
- milk;
- baby food;
- marmalade;
- cakes
Research has shown that overconsumption of products containing phosphorus compounds, especially carbonated drinks, can lead to health problems. It is possible:
- leaching of calcium from the body, which can trigger the formation of osteoporosis;
- violation of the acid-base balance - the additive can increase its acidity;
- the appearance of gastrointestinal diseases;
- exacerbation of gastritis;
- destruction of tooth enamel;
- development of caries;
- the appearance of vomiting.
In the non-food industry
The use of phosphoric acid can be observed in many areas of production. This is often due to the chemical properties of the product. The drug is used for the manufacture of:
- combined, phosphorus mineral fertilizers;
- activated carbon;
- phosphorus salts of sodium, ammonium, manganese;
- fire retardant paints;
- glass, ceramics;
- synthetic detergents;
- fire-resistant binding components;
- non-flammable phosphate foam;
- hydraulic fluids for the aviation industry.
- Lichen planus in the oral cavity - causes and symptoms, treatment regimen with drugs and folk remedies
- What the human liver loves and how to restore it
- Chicken with potatoes in the oven: recipes with photos
In medicine
Dentists use orthophosphorus composition to treat the inner surface of the crown. This helps improve its adhesion to the tooth during prosthetics. The substance is used by pharmacists to prepare medicines and dental cement. In medicine, the use of orthophosphorus compounds is associated with the ability to etch tooth enamel. This is necessary when using adhesive materials of the second or third generation for filling. Important points - after etching the surface it is necessary to:
- Rinse;
- dry.
Orthophosphoric acid. Properties and uses of phosphoric acid
Robert Boyle lived in the 17th century. At the same time, orthophosphoric acid . Are these facts related? Yes. It was Boyle who discovered the new compound.
An Irish chemist studied phosphorus by burning it and dissolving the remaining powder in water. So a new acid came out.
It is often called simply phosphorus. However, it is a generic name for several connections. Thus, HPO3 is metaphosphoric acid.
There is also pyrophosphoric with the formula H4P2O7. What is the chemical notation of orthophosphoric acid, we will understand in the first chapter of the article. As you understand, we are dedicating it specifically to the orthophosphorus compound.
Properties of phosphoric acid
Formula of orthophosphoric acid : - H3PO4. The prefix “ortho” indicates that the acid is oxygenic and that it contains the largest number of hydroxyl groups.
The least amount of them is in meta-compounds. The average number is in para-acids. Phosphoric has both meta- and para-isomers.
Note that all three prefixes are also used in the names of organic acids, to which orthophosphoric acid does not apply.
In organic chemistry, meta is a characteristic for substituents on a structural ring that are separated by one atom.
In para compounds the substituents are as far apart as possible, while in ortho they are neighbors. But, this is information, so to speak, for reference. Let's return to the discussion of the heroine of the article.
Externally, orthophosphoric acid is orthorhombic crystals. They are colorless and melt at 42 degrees Celsius.
However, due to the good solubility of the substance in water, chemists often deal with acid hemihydrate. Its formula: - H3PO4*0.5 H2O.
If the hemihydrate is crystallized, hexagonal prisms will be obtained. You can see them by taking a solution of orthophosphoric acid and cooling it.
A precipitate will form. This is a hemihydrate. Its melting point is 13 degrees lower than that of pure acid.
Acid mixes with water in any ratio. The reason lies in the system of connections with the liquid.
The molecules of the heroine of the article willingly join with her, while disconnecting from each other.
That is, in water, the compound breaks up into a mass of individual fragments that create hydrogen bonds with the structural elements of the liquid.
If we consider the structure of pure orthophosphoric acid , then it is a macromolecule. The individual molecules in it are connected to each other.
Hydrogen bonds are strong and reliable. This affects the physical properties.
The monolith conducts electricity poorly and is almost incapable of diffusion, that is, penetration into other substances.
If pure orthophosphoric acid melts, the liquid becomes viscous and oily - the molecules of the compound do not want to let go of each other.
In solution, the heroine of the article can be an electrolyte of medium strength. The internal structure of the molecules of the orthophosphorus compound does not allow one to reach the highest level.
The lengths of bonds between atoms in it are atypical. According to the formula, a double junction is formed between phosphorus and oxygen.
But, calculating the bond length, we get 1.74, that is, a number that is not a multiple of two. The length of the single bond between oxygen and hydrogen, on the contrary, is longer than expected - 1.3 instead of 1.
It turns out that the electron density of the P=O bond is partially distributed over other bonds.
The absence of a sharp difference in bond lengths leads to a non-standard structure of molecules. Their shape is close to tetrahedrons, that is, pyramidal.
Due to this structure, the reaction of orthophosphoric acid with most substances is impossible and proceeds slowly.
In chemical terms, the heroine of the article is passive, no match for sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, with a sharp difference in the lengths of intramolecular bonds.
Of the possible chemical reactions, the determining one for an orthophosphorus compound is interaction with silver nitrate.
A yellow precipitate forms. In other phosphoric acids it is white, so we can easily move the meta- and para-compounds aside and begin to study the process of producing orthophosphoric acid.
Phosphoric acid production
The heroine of the article is obtained from phosphates. These are esters and salts of phosphoric acids. Sometimes potassium orthophosphate with the formula K3PO4 is used.
But, more often, condensed phosphates are used. They have more than one phosphorus atom.
Phosphates, in turn, are extracted from phosphorites. This is a natural raw material, or more precisely, a group of minerals.
The most common ones are used. There are two of them. One is apatite, and the second is phosphorite, after which the group of stones is named.
We will analyze an example of obtaining the heroine of the article using a combination of calcium phosphate and hydrogen sulfate. The reaction is written as follows: - Ca3(PO4)2 + 3H2SO4 à 3CaSO4 + 2H3PO4.
In addition to phosphates, phosphorus pentochloride is also used. It is also called phosphoric acid chloride.
To obtain the latter, hydrolysis is sufficient, that is, interaction with water. The reaction is: - PCL5 + 4H2O à H3PO4 + 5HCl.
Phosphorus oxide is also forced to interact with water. It is produced by burning element 15 in the presence of oxygen.
The interaction of the oxide with water produces two molecules of ortho-acid, which means that this reaction is the most favorable and has no by-products. Let us be convinced by looking at the chemical record of the process: - P2O5 + 3H2O à 2H3PO4.
Note that phosphorus oxide reacts violently with water. In order to slightly “pacify” the release of heat and seething, the feedstock is treated with a concentrated solution of the already obtained acid. The concentrate must be heated to 200 degrees Celsius.
Application of phosphoric acid
Removing phosphoric acid from a person's life can cause collapse. The compound is used in at least seven industries.
In the food industry, the acid is called E338. Treatment of products with orthophosphoric acid fixes their color and does not allow it to be changed. This is largely due to the fact that the additive stops oxidation processes.
E338 is an antioxidant, unlike many foods, and is useful, just like phosphorus itself. In the body it is included in phosphatases.
These are enzymes without which cells cannot function normally. Normal taste without E338 is also not always obtained.
The additive gives dishes a pleasant sourness or spiciness. The specific taste depends on the amount of acid in the product and its concentration.
Now, let's remember spicy and sour dishes. In first place, perhaps, is soda. There are horror stories on the Internet about a nail that can corrode Coca-Cola if it sits in it for a week.
The horror story is not science fiction. However, gastric juice can do the same thing, and faster.
The acidity of the same Coca-Cola is 2.8, and the norm for the extract in the stomach is 1.3. The lower the number, the more corrosive the juice.
Phosphoric acid reacts with metals, like most acids.
That is why, over a long period of time, the compound can dissolve a nail and that is why it is used in cleaning mixtures.
This refers to products for removing rust and polishing metal surfaces.
Phosphoric acid for rust is most often used in everyday life, when restoring objects.
At the same time, the reagent is also used in large-scale production. Metallurgists make fluxes based on orthophosphorus compounds.
They facilitate the separation of gangue from the ore and reduce the melting point. Accordingly, fluxes are needed when soldering.
Orthophosphoric acid also available in the pharmacy . The substance is part of remedies for urolithiasis.
In addition, the heroine of the article is used by dentists. They need the reagent to etch the enamel before filling, as well as to treat the inside of the crowns.
The acid partially dissolves the metal base of the dentures. Pores appear in it, into which the fastening cement enters. As a result, the connection between the crown and the tooth is as strong as possible.
Orthophosphoric acid is part of freons, and they, as you know, are the basis of freezing units.
The heroine of the article is also the basis for many cosmetic products. In them, the acid stabilizes the chemical bonds between the constituent elements.
The compound performs a similar function in household detergents.
Let's add orthophosphoric acid to the list in hydraulic fluids for aircraft, in fertilizers, even in molecular research by biologists.
The latter use a reagent to clarify tissue sections examined under a microscope.
Don’t forget that phosphorus glows in the dark, which means phosphoric acid can brighten up gray everyday life. How much will you have to pay for this? The answer is in the final chapter.
Phosphoric acid price
Orthophosphoric acid is usually offered in solutions. The main concentration is 85%. Pour into canisters of 25, 30, 32, 40 liters.
The price tag is per kilo. On average, it is 80-110 rubles. The maximum price tag reaches 150 rubles per liter. The minimum request from sellers is 43 rubles.
It is worth considering that the cost depends on GOST a. Orthophosphoric acid 6552-80 pure, suitable for the food industry, reagents, and cosmetics industry.
But, there is also technical fluid. It is yellowish, which indicates the presence of contamination. GOST technical acid – 10678-76.
In retail, phosphoric acid is sold in small tubes. So, 50 milliliters for soldering costs about 100 rubles.
The rest of the products contain many additional elements. In agricultural fertilizers, for example, in addition to orthophosphoric acid, there is a complex of other minerals.
Therefore, the price tag depends on their quantity and nature. The markups of promoted manufacturers come into play.
Therefore, the objective cost of an orthophosphorus compound is judged only by advertisements for wholesale purchases of a concentrated solution of the reagent.
Anti-rust application
A rust converter based on phosphoric acid creates a protective layer on the surface that protects against corrosion during further use. The peculiarity of using the compound is that it is safe for metal when applied. There are several ways to remove rust with phosphoric acid, depending on the size of the damage:
- etching with immersion in a bath or other container;
- repeated application of the composition to the metal with a spray gun or roller;
- covering the surface with pre-treated mechanical cleaning.
The orthophosphorus compound converts rust into iron phosphates. The composition can be used for washing and cleaning:
- rolled metal products;
- wells;
- pipeline surfaces;
- steam generators;
- water supply, heating systems;
- coils;
- boilers;
- water heaters;
- heat exchangers;
- boilers;
- machine parts and mechanisms.
Use of acid
The use of phosphoric acid is quite wide. It is worth considering the most popular methods of using it.
In medicine
It is used in dentistry during tooth filling to etch the enamel immediately before the start of the process. This procedure has its negative aspects, since it is impossible to control the depth and stage of enamel splitting, as well as their complete removal before filling. The substance remaining after such a procedure can reduce the strength of the protection and lead to the formation of acidic residues on the tooth enamel. This acid is added in small doses to tooth whiteners.
Removing rust from metal surfaces using the submersible method and surface application. Rust converter
The advantage of removing rust with phosphoric acid is that it removes corrosion from the metal and creates a thin film on them, protecting them from various external influences. After covering a metal surface with this substance, an active process of corrosion and absorption of iron oxide begins. Then a gray film of an oily consistency forms on the metal plane.
There are various methods for removing oxides, among which are the following:
- with complete immersion of the element in an acid solution;
- surface treatment using a spray, brush or roller;
- coating with a solution of a mechanically pre-treated top layer of metal.
The corrosion converter is an acid solution with various additives. There are these types of solutions, depending on the additives used in their composition:
- primers;
- modifiers-stabilizers;
- rust converters.
Type 1 includes primer EVA-0112, consisting of the main component and 85% solution of the substance. It acts as a base for painting.
The Tsinkar converter contains acid and salts of manganese and zinc. When used, rust is transformed into a dense protective layer. The alloying process takes place.
Phosphoric acid for metal
To clean or solder metal elements, you must perform the following operations. Before completely immersing a metal element in an orthophosphorus composition, it is first cleaned of various types of deposits on the surface, in particular fats. To do this, wash the part using a cleaning agent. After this, it is necessary to dissolve 150 ml of the substance in 1 liter of water and immerse the metal element in this solution for 1 hour, stirring the liquid from time to time for greater efficiency.
Then you need to wash off the mixture with a solution that consists of 50% water, 2% ammonia and 48% ethanol. After this, the element must be rinsed under running water and dried well.
Before applying the spray to the surface with a roller or brush, you should first clean the surface from rust. After application, you should wait a little, and then wash off the mixture with a neutralizing solution and dry the part.
Such procedures can be carried out with different metals, including aluminum.
Application in agriculture
In agriculture, phosphoric acid extracted from the ore is used as a fertilizer. When it gets into the soil and then into plants, it helps them withstand drought and frost. At the same time, the soil becomes more fertile and favorable for growing vegetables and herbs.
Use of acid in everyday life and food industry
The use of acid in everyday life implies its use to remove corrosion from various surfaces (with the exception of acrylic). It is suitable for processing enamel and earthenware surfaces. Before applying the orthophosphoric acid solution, the metal surface must be treated with a detergent. To prepare the solution, mix 1 liter of water and 200 g of the active substance, and then apply the mixture to the surface to be treated for 1-12 hours. After time, the mixture must be extinguished with a soda solution and washed off.
In food production it is used as an acidity regulator.
Interaction of phosphoric acid
The properties of an inorganic substance determine its interaction with other substances and compounds. In this case, chemical reactions occur. The orthophosphorus composition interacts with:
- salts of weak acids;
- hydroxides, entering into a neutralization reaction;
- metals to the left of hydrogen in the activity series with the formation of salt and the release of hydrogen;
- basic oxides, participating in the exchange reaction;
- ammonium hydroxide, creating ammonium hydrogen phosphate;
- ammonia to produce acid salts.
Rules for working with phosphoric acid at home
Phosphoric acid, like any other, is an aggressive compound. If used carelessly, it can cause quite severe long-healing skin burns, and its vapors cause dangerous damage to the respiratory tract. The substance often causes fires and explosions. Treatment of metal with orthophosphoric acid must be carried out very carefully. Therefore, you should work away from open flames.
Important! The room in which work with this substance is carried out must be well ventilated.
Safety precautions when working with acid
Orthophosphorus compound belongs to the class of hazardous substances and requires caution. Work with the composition must be carried out in a special room equipped with supply and exhaust ventilation, away from sources of fire. The lack of personal protective equipment is unacceptable:
- respirator;
- gloves;
- special clothing;
- non-slip shoes;
- points.
Contact of orthophosphorus composition on the skin or eyes is dangerous, and inhalation of hot vapors is harmful. This may cause burns, dizziness, vomiting, and coughing. In case of emergency you need to:
- remove clothing that has come into contact with the substance;
- rinse the affected area with running water;
- call a doctor;
- apply a loose bandage;
- Neutralize spilled liquid with alkali.
Precautionary measures
When working with any acids, the most important thing is your own safety. Phosphoric acid is no exception. Before using it, you need to make sure you have a prepared respirator and rubber gloves. After all, phosphoric acid is a rather dangerous chemical that causes skin burns. The fumes of this acid are no less dangerous: their action can lead to severe poisoning or burns of the respiratory tract. It is also worth remembering that phosphoric acid is highly flammable and can lead to a fire. It is for these reasons that most activities with this substance should be carried out outdoors or in well-ventilated rooms. The main thing is not to let the acid get on the skin, but if this does happen, you should immediately wash the affected area under running water. If a significant part of the skin has been exposed to a chemical burn, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to defeat scale? Advice from experienced housewives
To remove rust and scale at home, use a weak solution of phosphoric acid. It turns rust into a black coating, which can then be easily cleaned from a metal product. Orthophosphoric acid is also indispensable for removing scale from dishes.
Transportation rules
There are special GOSTs that stipulate the rules for transporting phosphoric acid, which is classified as dangerous goods. The substance can be delivered by any type of transport. The chemically active liquid is transported in tightly closed:
- steel tank trucks;
- bottles made of polyethylene, glass;
- plastic cubes;
- barrels;
- cans;
- rubberized railway tanks.
Safety precautions
As a non-flammable and explosion-proof liquid, it is a substance of the second hazard class in terms of its effect on the human body. When its maximum permissible concentration in the indoor air is exceeded, atrophic changes develop in the mucous membranes of the throat and nose, crumbling of teeth, coughing, and if it gets into the eyes and skin - burns and inflammation. When handling the drug, you must wear rubber gloves, a respirator and safety glasses, maintain personal hygiene, turn on the supply and exhaust ventilation or work in a fume hood.
If there is an acid spill that gets on your body, you must first get rid of the wet parts of your clothing. The affected area of the skin is irrigated abundantly with running water, and it is necessary to apply the liquid rather than rub it with wet wipes or a towel. A one-time rinse lasts up to 20 minutes; if the burning sensation recurs, the procedure is resumed. A loose gauze bandage is applied to the affected area and a doctor is called; if pain is severe, an analgesic is taken. Spilled acid is neutralized with alkali.
No matter how tempting the advertising may be, excessive consumption of foods and carbonated drinks containing phosphoric acid will certainly cause harm to health. Penetrating into the blood, phosphates worsen hemoglobin and density, wash calcium out of the body, and, as a result, lead to osteoporosis, destroy tooth enamel, contribute to an increase in acidity in the body and the occurrence of diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Price
Phosphoric acid can be purchased in pharmacies, hardware stores, and ordered through Internet sites. For industrial purposes, they are purchased in bulk at discounts. The average cost for Moscow in rubles is:
| Quantity, liter | Average price, rub. | |
| Food thermal | 1 | 400 |
| Technical 85% | 0,8 | 380 |
| 1600 | 13500 | |
| Soldering flux | 0,01 | 180 |
| 0,003 | 40 | |
| Food additive E388 | 1 | 85 |