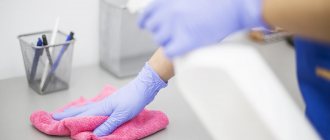
General definition
Routine cleaning of wards, routine cleaning of the office and other premises is one of the items on the list of measures and sanitary measures carried out for anti-epidemic purposes. First of all, routine cleaning of the ward and routine cleaning of other areas is aimed at preventing infection that may spread within the hospital.
The schedule and frequency with which routine cleaning of offices is done may vary - in addition to the two mandatory ones, additional cleaning and disinfection must be done between operations. In all cases when scheduled routine cleaning of premises is carried out, the following types of work must be completed:
- Cleaning from various passive contaminants. Dirt, dust, and other surface contaminants.
- Disposal of biological waste, especially carefully if routine cleaning of the operating room is carried out.
- Use of disinfectants. This is done without fail if all premises are being routinely cleaned; for operating rooms and wards, additional disinfection can be carried out in several stages.
Routine cleaning of hospital wards has the main goal of destroying microorganisms that can multiply on various surfaces and be the causative agents of various diseases, including serious ones.
Responsible algorithm after cleaning
The production participation of the junior medical worker must be noted in the logbook.
In it you can see who did the cleaning, the date, what products were used, and the signature of the person who cleaned.
Washing in an operating room is different from a regular ward. The peculiarity is that in the first case an exposure period after wiping with disinfectants is required for at least 30 minutes.
After disinfecting the premises, all equipment undergoes sterile processing until the next cleaning period.
Algorithm for current cleaning
Routine cleaning of premises is carried out at least 2 times a day, including cleaning and disinfection of floor surfaces, window sills, doors, furniture, and all equipment. Operating rooms undergo additional routine cleaning between surgeries. The use of only certified and safe cleaning and disinfectants is permitted.
When carrying out routine cleaning of premises, you must follow the principle:
- The first cleaning is done using detergents to thoroughly clean the surfaces from dirt and dust. The consumption rate of detergent additives is 50 grams per standard ten-liter bucket of water.
- The second cleaning includes the use of disinfectants. The concentration and composition are approved by the regulatory documents in force for the hospital.
Carrying out routine cleaning includes the following steps:
- Surface cleaning. To do this, you need to wipe all window sills, headboards, tables, other furniture and surfaces with a damp cloth or rag.
- A cleaning procedure is carried out in canteens or food centers for patients. After feeding, the distributor must wipe all tables, bedside tables and other surfaces.
- After cleaning the furniture and window sills, the floor is washed. In this case, the addition of a disinfectant solution is used.
- If necessary, additional quartzing is performed. This procedure is mandatory for routine cleaning of operating rooms.
- The final stage includes ventilation.
The used cloth used to wipe the surfaces is disinfected. To do this, the composition of the disinfectant solution is diluted in accordance with the approved hospital standards. After disinfection, the fabric or rags are rinsed or washed with running water until the smell of the disinfectant disappears. After this it is dried.
Equipment and cleaning products
Since the purpose of cleaning in health care facilities is not only to remove contaminants, but also to disinfect surfaces, the work will require professional cleaning products and special disinfectant solutions that have antimicrobial and antibacterial effects. In addition, each type of work requires special equipment:
- 2 containers each for surface treatment (for washing floors, walls, equipment, furniture);
- window cleaning containers;
- 2 mops (for walls and floor);
- 2 rags (sterile and non-sterile);
- floor cloth;
- 2 brushes for radiators;
- bactericidal lamp;
- overalls (gloves, apron, robe, mask, cap) and safety shoes.
Reusable items should be labeled to indicate their purpose. As for sterile rags, they will be required for general cleaning of aseptic and sensitive rooms.
When working with disinfectant solutions, you must follow safety rules according to the instructions on the packaging. The preparation of solutions must be carried out in accordance with the standards and recommendations specified in the instructions. On average, the consumption of such products is 100-150 ml per 1 square meter of surfaces.
Registration logs for current cleaning
The log of current cleanings includes an approved schedule for their implementation. After cleaning, a recording is made. The log indicates the planned date and time, actual data, who carried out the cleaning, what detergent was used, the disinfectant solution, its quantity and concentration. This must be followed by the name of the person who controlled the process and effectiveness. Paintings are put up of those who did and supervised the cleaning.
A regulatory document is drawn up separately, which indicates the number of cleanings for each specific type of room and lists individual rooms for which there is a personal schedule.
Handling and storage of cleaning equipment
Maintenance of cleaning equipment is an integral part of the cleaning process and includes washing and disinfection, as well as proper storage of clean equipment. Poorly treated rags, cleaning containers and mops accumulate microorganisms and themselves become factors in the transmission of infection.
Sanitary rules SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 (clause 11.5 of section 1) provide for the possibility of processing mops and rags in washing machines specially designated for these purposes, which are installed in places where cleaning carts are assembled.
A separate room must be allocated for storing cleaning equipment (clause 11.5 of section 1 of SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10), equipped with racks or other devices for fixed storage of mops, containers and rags.
Thus, the cleaning process is one of the key links in the prevention of nosocomial infection. Despite the ordinary nature of the cleaning process, medical organizations face significant difficulties in organizing it. Solving these problems is possible with an integrated approach and the development of step-by-step algorithms and visual instructions for personnel performing cleaning and maintaining cleaning equipment in each specific medical organization.
Wet cleaning of the office
An algorithm for wet cleaning of the treatment room has been developed. It is preferable to perform it using the so-called mop technique, which cannot cause harm. A mop is a tool prepared in advance, with which wet sanitation is carried out. The mop method has the following features:
- For each individual office in which tidying will take place, it is necessary to prepare the required number of napkins, mops and other equipment.
- The equipment cannot contradict the sanitation requirements of a particular medical office.
- Inventory must be marked with stickers of different colors according to the type of work or room. This helps make the tool selection process much easier.
- All prepared mops and napkins must be treated in advance with a disinfectant solution (0.05 ml of the drug for each napkin, 0.25 ml for each mop).
- The equipment that has been prepared is placed on a special cart for sanitation.
The algorithm for routine cleaning of the treatment room involves washing using equipment and supplies that are specially designed for use in medical institutions. To create it, materials are used that ensure the comfort of the procedure and a long period of operation even with active daily use.
Napkins and mops are also allowed to be used repeatedly, but only if they are systematically washed and disinfected. The final cleaning algorithm for the treatment room is also based on this method. The Mop method is a selection technique. But it makes it possible not only to guarantee compliance with sanitary epidemiological requirements in medical institutions, but also leads to a reduction in the burden on medical personnel. It reduces the risk of developing musculoskeletal diseases and other occupational pathologies.
In addition, the “non-bucket” method of wet cleaning of the treatment room allows a medical institution to significantly reduce costs associated with the purchase of new equipment and the purchase of consumables. By following the rules for cleaning the treatment room, you can achieve ideal sterility of the room, equipment, and instruments.
Types of cleaning
The treatment room is cleaned daily and thoroughly. Sanitation, which takes place every day, is divided into subtypes:
- Preliminary. It takes place before the start of the morning shift and includes dusting furniture and medical equipment.
- Current. Consists of removing dirt throughout the day (at least 2 times a day).
- Final. Takes place at the end of work.
General sanitation is performed at least once every 7 days. In rare cases, it is possible once every week and a half.
How to clean and disinfect in an educational organization
The main thing in the article
- Clean and preventively disinfect the school daily.
- If an infection is detected in the school, organize ongoing and final disinfection.
- Cleaning equipment should be washed and disinfected regularly in a dry-heat oven.
- Use only products approved for child care facilities for cleaning and disinfection.
Disinfection is an effective preventive measure to prevent diseases. In educational organizations it is carried out to disinfect premises, dishes, linen, toys, and food products.
What are the types of disinfection?
1
once a month
schools are required to carry out general cleaning of premises using detergents and disinfectants
There are three types of disinfection:
· preventive;
· current;
· final.
The purpose of preventive disinfection is to prevent diseases among children and workers. It is carried out daily. If an infection is detected in a kindergarten or school, ongoing disinfection is carried out for a certain period, and a final disinfection is carried out before restrictive measures are lifted. Their goal is to prevent the disease from spreading.
The requirements for disinfection measures are contained in SP 3.5.1378–03, approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation on 06/07/2003. Separate standards are specified in the sanitary rules for kindergartens and schools.
Who has the right to carry out disinfection measures?
Preventive and ongoing disinfection is carried out by specially trained employees of the educational organization, and final disinfection is carried out by specially trained employees or an organization that is engaged in disinfection activities.
If you carry out current and final disinfection on your own, the process must be carried out under the supervision of sanitation workers and the disinfection station.
A medical office can be disinfected if the educational organization has a license for medical activities. You can disinfect other premises without a license. This is stated in the letter of the Russian Ministry of Health dated 06/09/2016 No. 14–5/993.
How to disinfect in case of infectious diseases
Disinfection measures depend on the disease recorded in the educational organization. For parasitic diseases, be guided by the provisions of SanPiN 3.2.3215–14, approved by the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated August 22, 2014 No. 50; if scabies is detected, follow the norms of the Guidelines for Medical Disinsection R 3.5.2.2487–09, approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation 02/26/2009.
Don't forget to study regional and municipal documents. For some diseases, federal legislation requires only routine disinfection, but local authorities have the right to determine the need for final disinfection.
Example. In Moscow, when scabies is detected, both current disinfection and final disinfection must be carried out by the disinfection station. This is stated in the order of the Moscow Department of Health dated September 26, 2005 No. 383 “On improving measures for the prevention of scabies and dermatomycosis.”
If any disease is detected, carry out routine disinfection. Disinfect common areas, offices, dishes, and linen if necessary.
note
A child with suspected infection should be isolated and then transported to a medical facility as quickly as possible
Wet clean floors and surfaces with disinfectants.
Purify the air in offices, including ultraviolet irradiation. Use ultraviolet bactericidal irradiators and installations for this purpose.
When the bactericidal lamp is switched on, it does not emit ozone, so its use is safe for the respiratory system, and rooms with continuously operating bactericidal lamps do not require ventilation. Closed type irradiators are allowed to be used in the presence of people, open type - only when no one is in the room. It is more convenient to use mobile bactericidal irradiators.
Carry out routine disinfection measures systematically while there is a danger that the infection will spread.
Carry out final disinfection after the sick person has left the building of the educational organization or before lifting restrictive measures (quarantine), especially carefully in the foci of those diseases whose pathogens are resistant to environmental factors (salmonellosis, polio, helminthic infestations, pediculosis).
When organizing disinfection measures, take into account the instructions of the Rospotrebnadzor authority. If you don’t have enough strength and resources, hire specialists from a disinfection station.
Before the final disinfection, the medical worker of the educational organization or the head of the disinfection team inspects the premises, finds out the epidemiological situation, determines the volume, content and sequence of disinfection measures, and selects a disinfectant. Then the employees who will carry out disinfection measures:
Important document
Which disinfectants belong to hazard class IV, is stated in GOST 12.1.007–76, approved by Decree of the USSR State Standard of March 10, 1976 No. 579
· prepare solutions of disinfectants;
· disinfect epidemiologically important objects (sputum, secretions, food debris, dishes, linen), select items that are subject to chamber disinfection;
· destroy insects if they are found in the outbreak of the disease;
· disinfect objects collected from places where the patient was present.
Methods and means of final disinfection depend on the objects and surfaces that require treatment.
Example. To disinfect linen means to boil and iron it on both sides. Woolen blankets, carpets, mattresses, rugs, curtains are vacuumed, then dried in the sun and ironed with a hot iron through a rag. Dust from vacuum cleaner containers after neutralization is disposed of in the general sewer system.
What equipment is suitable for cleaning and disinfection?
Cleaning and disinfection are carried out with marked cleaning equipment. After use, it is washed with hot water and detergents and dried.
To soak dishes in a disinfectant solution, use a marked container with a lid; for disinfection, use a dry-heat oven.
To carry out current and final disinfection, you will need:
· hydraulic remote control;
· buckets with measuring marks;
· brushes for cleaning soft things;
· sprayers of powders and liquids;
· bags for transporting things to the disinfection chamber;
· oilcloth bags for clean and used rags and for used sets of workwear;
· personal protective equipment (goggles, rubber gloves).
Where can I see the list of approved disinfectants?
The list of detergents and disinfectants that are approved for use in educational organizations is not approved by regulatory legal acts. The letter of Rospotrebnadzor dated January 25, 2006 No. 0100/626-06-32 indicates some disinfectants with antiviral effects registered in Russia.
Frequency of cleaning and disinfection at school
| View | Periodicity | Base |
| Wet cleaning of toilets, dining rooms, lobbies, recreation areas | After every change | Clause 12.3 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Dining room cleaning | After every meal | Clause 5.3 SanPiN 2.4.5.2409–08 |
| Wet cleaning of educational and auxiliary rooms with open windows or transoms | After finishing classes or shift. The break between shifts must be at least 30 minutes. In case of unfavorable epidemiological situation, the break for disinfection treatment is increased to 60 minutes | Clauses 10.13, 2.3 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Sanitation of food processing equipment | Every day when dirty and at the end of work | Clause 5.14 SanPiN 2.4.5.2409–08 |
| Disinfection of toilets, showers, locker rooms, walkways, benches, door handles and pool handrails | Daily, according to cleaning and disinfection schedule | Clause 3.9.1 SanPiN 2.1.2.1188–03 |
| Cleaning toilets, showers, buffets, medical premises using disinfectants | Daily | Clause 12.8 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Cleaning of boarding school premises (if any) | Daily | Clause 12.3 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Disinfection of sanitary equipment | Daily | Clause 12.8 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Treatment of sports equipment with detergents | Daily | Clause 12.15 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Cleaning carpets using a vacuum cleaner (in primary schools, after-school groups, boarding schools) | Daily | Clause 12.16 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Change of bed linen and towels | When dirty, but at least once a week | Clause 12.7 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| General cleaning of all premises of the school and boarding school (if any) | Monthly | Clause 12.6 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Cleaning exhaust ventilation grilles | Monthly | Clause 12.6 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| General cleaning of all premises, equipment and supplies of the catering department, followed by disinfection | Monthly | Clause 5.18 SanPiN 2.4.5.2409–08 |
| General cleaning of the pool premises with preventive repairs and subsequent disinfection | Monthly | Clause 3.9.2 SanPiN 2.1.2.1188–03 |
| Processing bed linen in a disinfection chamber | Before the start of the school year | Clause 12.7 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Disinfection of medical instruments in the medical office | In accordance with the instructions for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical devices | Clause 12.9 SanPiN 2.4.2.2821–10 |
| Disinfection of dishes and equipment | According to epidemiological indications in accordance with the instructions for the use of disinfectants | Clause 5.17 SanPiN 2.4.5.2409–08 |
Only disinfectants of hazard class IV are allowed for use in educational organizations. Most often, they contain cationic surfactants (surfactants) and polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride (PHMG chloride) as active ingredients.
e.rukobr.ru
In No. 2, 2022 of the electronic magazine, read an article on how to wash dishes taking into account sanitary rules and regulations
The disinfectant must have:
· state registration certificate;
· certificate of conformity of the GOST R system;
· manufacturer's instructions.
Read the instructions carefully. It should contain:
1) an indication of the possibility of using the product in kindergartens and schools;
2) toxicological characteristics of the product and its working solutions;
3) information on the preparation of such solutions (calculations for the drug or the active substance), precautions when working with the product, storage conditions, packaging requirements.
Disinfectants must be changed periodically to prevent the emergence of strains of microbes resistant to them.
+
FOR YOUR INFORMATION
How to store disinfectants
Store disinfectants in their original packaging in a dry, dark, cool place, out of reach of children, away from medications and food products.
Keep flammable, combustible, explosive liquids away from heat sources and sunlight. Such places can be closed cabinets in the bathroom, basements and technical rooms.
Keep the packaging safe. Do not allow undiluted substance to enter wastewater, surface or ground water or sewer systems.
Consumption standards for detergents and disinfectants for educational organizations have not been established at the federal level. Check to see if such a document was developed by local governments. If not, determine the standards for the educational organization and approve them by order of the head. As a basis, take the approximate consumption rates approved by order of the USSR Ministry of Education dated January 28, 1986 No. 45. The regulatory legal act has lost force, but it can be used as an example.
Download! SanPiN: Current cleaning in health care facilities. Algorithm according to SanPiN
Click on the picture to enlarge
Click on the picture to enlarge
Health care facilities are a special type of premises in which cleanliness and order should always be at their best. In order for routine cleaning at such facilities to achieve high-quality results, it is recommended that it be carried out in accordance with current standards and sanitary rules.
Only if this condition is met will the medical institution be truly clean, which is one of the main conditions for the safety of the employees and patients themselves.
Attention! Do not forget that you should also carry out general cleaning in the health care facility. The rules for such cleaning differ from those that will be described in this article. If you are interested in the algorithm of actions for general cleaning, read this article: