Fleas are blood-sucking arthropods found throughout Russia. In the Central region, Moscow and the Moscow region there are several species of these pests that can parasitize:
- people
- Cats
- Dogs
- Rodents
- Birds
Not so long ago, it was believed that rat fleas live only on rats, dog fleas only on dogs, cat fleas only on cats, and so on, but recent research in the field of entomology has proven that fleas living on warm-blooded animals do not hesitate to bite people, either. who are close to these animals.
This discovery was made immediately regarding several of the most common types of fleas. Fleas live all over the world and, depending on environmental conditions, have completely different characteristics. Here we review and describe the key characteristics of the most common and harmful fleas for humans specifically for the Central region of Russia. You can read more about each type of flea separately here
.
Fleas:
- They feed only on the blood of people and animals, but do not live directly on them
- They are carriers of several types of typhus, plague, leprosy, hepatitis B and C, tick-borne encephalitis and a number of intestinal parasites
- They move by jumping and are able to cover a distance of up to 2 meters at a time
- They always breed indoors en masse, but do not live in organized colonies
- After a bite, a flea can become saturated with blood from several minutes to several hours.
Structural features
The body of fleas is laterally compressed, narrow, smooth , equipped with bristles and spines that help them move and stay in the thick fur and between the feathers of their hosts, in the folds of clothing, as well as in the substrate of their nests and burrows. The head and chest often have serrated ridges ( ctenidia ).
The size of fleas of different species varies
from 1 to 5 mm , but in females of some species it can reach 10 mm due to hypertrophic growth of the abdomen after the start of feeding.
The antennae are always located behind the simple eyes and, at rest, are placed in special recesses - antennal fossae.
The antennae may be used by males to hold onto a female during copulation . The oral apparatus of fleas is of the piercing-sucking type .
It is characterized by the transformation of epipharynges (unpaired stylet) and lacinia (paired stylets) into stylets, articulated with the maxillary lobes.
The lower lip with a pair of labial palps is transformed into case flaps for the components of the proboscis. The mandibles in adult fleas are completely lost . The chest is equipped with strong limbs, providing the insect with rapid movement in the host's integument and the ability to stay on rough surfaces at any angle.
They often move by jumping, using the second and especially the third pair of legs to push. In the posterior part of the abdomen, behind tergite VIII, there is a unique sensory organ found only in fleas - the abdominal sensillium, or pygidium , equipped with trichobothria (tactile hairs) and capable of detecting air vibrations .
Based on the nature of changes in ploidy, the following types of life cycles :
- Haplophasic : the organism has a single set of chromosomes (n, haploid) throughout the cycle; These life cycles are characteristic of many bacteria and protists that do not have a sexual process.
- Haplophasic with zygotic reduction : after the formation of the zygote (2n), meiosis occurs and the remaining stages of the life cycle are haploid (this life cycle is characteristic of many green and other algae, as well as most other groups of protists and fungi).
- Diplophase with gametic reduction : all stages of the life cycle are diploid (2n), only gametes are haploid (n) - a life cycle characteristic of multicellular animals.
- Haplo-diplophase : at both diploid and haploid stages, mitotic divisions occur, leading to reproduction or growth, and the life cycle contains diploid and haploid generations - a life cycle with intermediate (sporic) reduction, characteristic of all higher plants, as well as foraminifera and some other protists.
By the number of generations (ontogenies) in the life cycle:
- Simple : the cycle includes one generation.
- Complex : cycle includes two or more generations; such a life cycle is characteristic, for example, of many cnidarians (alternating generations of polyps and jellyfish), for most trematodes (alternating generations of marites, sporocysts and redeyes).
Doggystyle
They are less common than felines and do not reproduce as quickly, but they successfully infect all four-legged animals that come their way. Like all other types of pests, dog parasites have a flattened body and dark color .
Under a microscope, the insect's too-long hind legs attract attention. It is they who ensure jumping at distances that exceed the size of the parasite by a hundred times.
REFERENCE : The oldest jumping insect was found in fossilized amber, which is more than 55 million years old.
Dog fleas successfully prey on humans . This especially happens when the animal is heavily infected. Pets can pick up the pest from an infected dog during a walk, from a cat or rat, and even from a person whom the parasite was used for “transportation”.
Dog fleas
Appearance
You should immediately understand that fleas are insects that are parasites on the skin and hair of animals living near you. They are used to sucking the blood of rabbits, cats, dogs, chickens, parrots, hamsters and rats.
However, the worst thing is that these small creatures are capable of causing harm directly to humans . Using a special piercing-sucking apparatus, the flea pierces an inconspicuous hole on the surface of the skin of its owner and is saturated with his blood.
The signs by which you can recognize an insect are a smooth body, which has a narrow texture and is somewhat flattened on the sides . It is also worth paying attention to the bristles and small spines that are located throughout the body and serve to ensure that the flea is able to move and stay on the fur of its victim.
The insect's head and chest are covered with so-called serrated combs or ctendia . As for the size of an adult, it ranges from 1 to 5 millimeters. And females that have had enough time sometimes reach 10 millimeters in length.
The flea's head is equipped with special antennas, which, when not needed, hide in antennae pits, and when the insects go hunting, they reappear in order to detect the most vulnerable spot.
How many legs does a flea have? The flea makes its jumps with the help of three pairs of fairly strong paws , which are located on the belly. The sensory organ, which is located on the back of the body, is designed to instantly capture air vibrations in the environment.
Today there are about 1000 species of these insects. Another interesting fact is that representatives of this family often lack vision or have the simplest manifestations of it .
Read more about such types as: human, earthen, bed, herbal.
Studying the life activity of fleas and the characteristics of their body is possible only with the help of a microscope. The largest collection of specimens is in the British Museum. It was collected in Tring by scientists N. Rothschild and K. Jordan.
Flea lifespan
How long does the most common human flea, Pulex irritans, live? In a favorable environment, this insect lives for about 3 months.
During this period, 1 female of this bloodsucker lays 400–600 small eggs, and each such small pest makes about 100 bites. Only after this minimal “plan” is completed does this parasite die naturally.
An important condition for comfortable living of fleas is compliance with specific air humidity and temperature. Thus, rat-like insects Xenopsylla cheopis live quietly inside any room at 14 degrees Celsius and 55% humidity or more.
Bloodsuckers that live in a private household or apartment (Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis) also feel good there. However, they die quickly without immediate access to blood.
If these insects live in places with elevated temperatures, then all their phases of reproduction and development pass much faster. Thus, adults become very large.
Typically, flea larvae of pulex irritans degenerate into an adult in 30 days, while at elevated temperatures the fleas multiply and then grow much faster - in 7 days. The development of flea eggs ends after 14 days, and then for another 14 days this small pest is in the pupal phase.
These bloodsuckers, who live not in a warm home, but in nature, die quickly. After all, they are destroyed by the carriers themselves (dogs, cats, etc.). Then the animals bite the bloodsuckers out of their fur.
Also, many such bloodsuckers die from various infections. There are fleas that change several hosts during their life when the animal dies.
Fleas Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis immediately leave a dead dog or cat because they cannot feed on the blood of a dead animal.
How long do these insects live?
How long do various species of bloodsuckers live (for example, Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis, Xenopsylla cheopis, etc.)?
The lifespan of all types of fleas is directly related to these 3 factors:
- specific temperature regime;
- living conditions - apartment or street;
- air humidity.
On average, these small pests live 18–90 days. Throughout its life, 1 bloodsucker makes about 10 bites and, thus, it injures its owner.
Over the course of her entire life, a female flea lays about 500 eggs.
However, these bloodsuckers often die from various infections that they themselves spread, as well as from the teeth of a domestic cat or dog, from human hands or any disinfectant.
Can parasites live without food?
How long do fleas live without food? Approximately 2–3 months. the parasites Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis or Xenopsylla cheopis can live without consuming blood.
Especially those individuals that often bite humans. At the same time, they remain mobile.
However, if these insects do not feed for a long time, they do not reproduce in any way. After all, only after a hearty lunch do they mate with each other, and then the female flea lays many small eggs.
Do these bloodsuckers live in a private household or apartment if there are no animals or people there? Yes, but not indefinitely. Sooner or later they still die.
What determines the lifespan of a flea?
At the moment, it is the sharp change in air temperature that greatly affects the lifespan of fleas.
In addition to it, the lifespan of such bloodsuckers Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis or Xenopsylla cheopis is directly related to the following factors:
- air humidity. Low (but not too low) humidity is comfortable for bloodsuckers;
- source of food. Small pests that do not receive fresh animal or human blood for a long time live longer;
- the invariability of specific temperature and humidity conditions.
Bloodsuckers that live in areas with constant sharp changes in humidity and fluctuations in street temperature often quickly become numb. This significantly increases the life span of a flea.
An important factor for fleas is the number of offspring produced from 1 female, and not the rate of formation of flea larvae. As a rule, such a process is continuous.
Thus, while fighting various bloodsuckers, the lodger not only removes these parasites from the pet’s fur, but also destroys flea larvae hidden in secluded places.
Photo
What a flea looks like, close-up photo:
Where do fleas live?
A very large number of flea species are determined by suitable climatic conditions. It is a common belief that the number of fleas varies depending on the time of year.
When a cold period sets in, the number rarely decreases, and, conversely , with the arrival of warmth, insects actively reproduce. The hot months of summer seem to be especially active in this regard.
The greatest danger comes from fleas that live in the apartment and can cause harm to them. Fleas often settle near rodent burrows . As for residential premises, they are most often found in small cracks on the floor , under bedspreads and in dusty places where people cannot penetrate.
Find out where fleas come from in the house?
Remarkable is the fact that a female flea is capable of laying about 400 eggs in her entire life.
How bloodsuckers get into an apartment
Will fleas live in the apartment in winter or not? Most likely not, because they are more likely to start in residential areas in the summer or autumn. At the same time, they often inhabit the lower floors of apartment buildings or private households.
Ground-like insects inhabit very dusty rooms or abandoned various buildings.
The fleas Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis enter an apartment or private house in this way:
- from the entrance of an apartment building;
- enter the home from neighbors;
- they are brought in by domestic animals;
- They infect a certain home with various rodents.
If the basement is always damp, then flea breeding often begins in this place. After all, the most common human flea, Pulex irritans, loves dampness. Also, these small pests multiply quickly inside well-heated living spaces.
If a person does not ventilate his apartment for a long time, and there is always a lot of garbage in it and sunlight does not enter inside, then the bloodsuckers Pulex irritans quickly infest and multiply in this home.
Due to their small size, these parasites enter the home through small cracks in the apartment.
In addition, various species of fleas (for example, Ctenocephalides canis, etc.) do not always live on their host. They live comfortably on baseboards, floor crevices, linoleum, carpet, as well as on pieces of furniture, clothing or a variety of soft toys.
Video
Flea infestations of your pet and home
Fighting methods
The fight against this misfortune should begin with a number of special measures that can stop the reproduction process and neutralize already born individuals. If there are animals in the house, then it is necessary to treat their fur with special products .
Shampoos and a variety of medications are sold in pet pharmacies especially for these purposes . A very good assistant in this matter is pyrethrum , which veterinarians strongly recommend treating the hair of cats and dogs.
It can also be used to treat all possible places where pests accumulate directly in the home. Folk remedies include sweeping floors with a wormwood broom . A flea collar is also actively used.
Dangers posed by pests
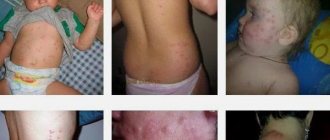
As a reward from bloodsuckers, people can get not only all sorts of local reactions on the surface of the skin, but also some dangerous diseases. They are carriers of tuberculosis, rat typhus, tularemia, listeriosis, and plague. Their consequences, if someone is unlucky enough to become infected with one of the ailments, can be very dire.
Scientists are confident that each insect is quite capable of giving people one of several hundred ailments that exist in the parasite’s body. There is no need to panic, because it is rare that a bloodsucker bite can lead to any disease. It is dangerous if bites appear on the body due to a sand flea. In this case, the risk of becoming infected increases significantly. With a strong bite, the affected area often transforms into an abscess. Bloodsuckers of this type are able to get under the skin and carry out reproduction there, as well as harmful life activities.
Video
Lifestyle
Adults differ from many other insects in having a fairly active lifestyle , which is marked by periodic settlements on the body of the prey in order to receive nutrition for further life activity.
What do fleas eat? These parasites drink blood. It is worth noting that when they are full, they most often leave the object and look for a new owner, which makes these insects potential carriers of various diseases .
for fleas to get enough food once a day , but if this process is interrupted for some reason, then they are forced to look for another source of nutrition.
How long can fleas live without food? If it is not possible to find a source of food, then a flea can survive without food for a week, or even a month . As for the host, these parasites are quite unpretentious .
Individuals that live on cats can consume the blood of a dog or human without much embarrassment. However, it is fair to note that fleas that live on chiropterans will never jump onto mammals .
Read more about the dangers of fleas for pets and people here.
Why are these bloodsuckers needed?
At the moment, there are many species of fleas (Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis, Xenopsylla cheopis, etc.). Without these small pests, many animals would simply die out.
After all, these bloodsuckers are part of the specific food chain of various animals. Also, these bloodsuckers transfer various diseases from one carrier to another.
Thus, blood-sucking insects (fleas) are useful not for people, but for certain viral microorganisms.
The role of such a bloodsucker in nature comes down to the fact that it is a parasite. Thus, this insect shortens the life of its “carrier” (cat, dog, etc.).
In general, fleas have a positive meaning in nature, but they are more likely an epidemic. Often these small pests are the causative agents and first carriers of various epidemiological infections.
According to numerous laboratory studies by biologists, this bloodsucker simultaneously carries 30 types of specific viruses and bacteria.
Fortunately, not all such insects have the same ability to transmit various pathogens (plague, typhoid, etc.). It all depends on the diet, type and physical condition of the bloodsucker.
Flea Behavior and Identification
Fleas are quite active and sense the approach of danger very well thanks to sensory organs that detect the slightest shudders in the air. This is why it is almost impossible to neutralize a flea with bare hands .
There is a high probability that it will move to another owner and continue to be saturated with his blood. We should also not forget that most fleas are not on the animal itself, but in its environment, which complicates the process of pest control.
When purchasing a drug to exterminate parasites from a pet pharmacy, do not forget to inquire about their toxicity level for the animal and check the period of its action.
As you know, it is easier to prevent than to cure. Special animal collars that are impregnated with insecticides will help you with this.
Varieties
To date, scientists have described more than 2,000 species of fleas, which are grouped into 15 families. Fleas are found in animals, birds, and can live in the upper layers of the earth and on plants. A person can most often come into contact with the following species:
- felines are one of the most common species; they parasitize mainly on cats, but can also live on dogs, rodents, and other animals, and also bite people;
- canine fleas are close relatives of cat fleas, they are also not limited to the dog as a victim, they can settle on cats and other pets;
- human - can parasitize on humans, as well as on animals that often come into contact with them (cats, dogs, horses);
- rats - mainly parasitize rodents (rats, mice), small brown insects are very dangerous, as they carry pathogens of many dangerous infectious diseases;
- domestic - this is not a scientific classification, this is the name given to fleas that live in a person’s home; these include, for example, bed or linen fleas ;
- earthen - live on the ground or in the top layer of soil;
- arboreal - prefer to settle at the foot of trees;
- avian – most often parasitize birds, including domestic chickens;
- herbaceous (field) - live in the grass.
These are just a few species from the huge variety of fleas existing on the planet.
How long does a flea live?
The optimal temperature for flea development is 18–27 degrees, and the most suitable humidity is 70–100%. Under such conditions, the flea grows in 20–49 days .
If the humidity drops below 60%, then the larvae stop the development process, and they completely die in the water .
It is interesting that if environmental conditions cannot be called favorable, then the period when the flea remains sealed in a cocoon may be significantly longer.
The main part of fleas are temporary parasites that use domestic animals and humans only to get enough food in order to continue their life activities.
Reproduction
Complete metamorphosis is how fleas develop. This means that the egg that hatches as an adult first produces a larva. This larva then turns into a pupa. The larvae do not pose a great danger and are not capable of causing harm .
This is only a transitional stage, the final goal of which is an adult insect, which in the scientific world is called an imago. It is these latter that support their vital functions by feeding on the blood of animals and people.
An adult flea produces eggs that have a dry surface and usually fall into the insect's nest or onto the floor. The larvae, which emerge from the eggs after some time, are whitish in color and have no legs or organs of vision .
They can be observed in cracks in coverings or in carpets. If their direct carrier lives in the basement, then attention should be paid, first of all, to heaps of garbage and various household rubbish.
Flea larvae that threaten cats, dogs and humans sometimes settle on green lawns . There they have the opportunity to receive nutrition from plant juice.
Also, they are thus protected from the harmful effects of sunlight. Very often, owners of farms where pigs are raised become victims of fleas.
The egg development period ranges from several days to several weeks depending on environmental conditions. The life cycle of the larva is approximately two to four weeks.
When this period ends, the larva begins to construct a cobweb cocoon, which becomes its refuge until the time comes for rebirth into an adult flea, capable of obtaining its own food on its own.
Read more about flea reproduction.
The insect can remain in a clogged state for up to several months . It often happens that even the imago does not want to crawl out of the protective cocoon and does this only when it senses a potential victim.
Habitats of bloodsuckers in the apartment and in nature
Where do fleas live?
In an apartment, the parasites Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis settle and live for a long time in the following places:
- in bedding for domestic cats, dogs or other pets;
- on carpeted surfaces. Then flea eggs accumulate on the carpets;
- on sofa upholstery and outer covering of chairs;
- on a variety of soft toys for children;
- on old clothes;
- on mattresses;
- in bed linen;
- behind room or other apartment skirting boards;
- under the linoleum.
Outdoors, these small pests live close to a variety of animals (hamsters, rabbits, rats, etc.), which provide them with a source of food.
Fleas infest and lay their eggs and larvae in trash cans, basements, sand piles, bird nests, or inside the burrows of various animals.
Household fleas that live near people are divided into the following types of insects:
- bloodsuckers from pets - Ctenocephalides felis and Ctenocephalides canis;
- rat or mouse parasites - Xenopsylla cheopis, etc.;
- ground or basement bloodsuckers - for example, Vermipsylla alakurt;
- bed insects, etc.
Such bloodsuckers are small insects that cause a lot of problems for animals or humans. Their bites are very painful, after which itching and skin irritation form on the fur of a cat or dog, as well as on human skin.
In addition, the bloodsuckers Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis carry many unpleasant ailments. Therefore, it is important for a person to get rid of them in a timely manner - to destroy not only the fur of pets, but also to remove them from open or hidden corners of the apartment.
Can small pests live on the sofa and on clothes?
At home, the most common human flea, Pulex irritans, often lives on sofas, carpets, clothing or bedding. They also live behind room and other baseboards, as well as in wall cracks.
These small pests Pulex irritans like to live in comfortable conditions.
These bloodsuckers love to live and copulate on the warm carpet pile, where they sit out after satiation.
In ancient times, rich people made such anti-flea traps: they hung small pieces of natural concrete wool on their bare legs to lure bloodsuckers Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis, and then burned them.
Can bloodsuckers live on the body and on human hair?
Unlike various lice, human fleas Pulex irritans, which are infested in a private house or apartment, do not live on the skin or hair for a long time. After all, after being saturated with human blood, they immediately leave the human body.
If the bloodsucker is distracted while eating, it lingers for some time on the clothing on the underside.
Sometimes these small pests remain on summer or other clothing for 1–2 days. Then the Pulex irritans fleas periodically bite the person. However, they do not use humans as their daily hosts because little hair grows on them.
Laboratory studies by biologists have shown that bloodsuckers Pulex irritans live and reproduce quietly after consuming human blood. But more often, these small pests rarely attack people, and also do not copulate on their body.
The fact is that these insects are immediately very noticeable on human skin, and people immediately shake them off. In addition, it is difficult for them to move around a person, because their bristly small body is adapted to a comfortable life only on thick animal fur.
Human fleas, Pulex irritans, do not typically lay multiple eggs in hair. Firstly, these small pests often simply do not reach the head - they jump at most to ankle level.
And secondly, when they come into contact with a person, such bloodsuckers immediately bite him, and then immediately get out of the way.